Java: Variables used in lambda should be final or effectively final In Java, a lambda expression can reference a variable outside the expression itself. It can reference:
local variable(should be final or effectively final)
instance variable
static variable
Reference a local variable If a expression references a local variable, the local variable should be final or effectively final. For example:
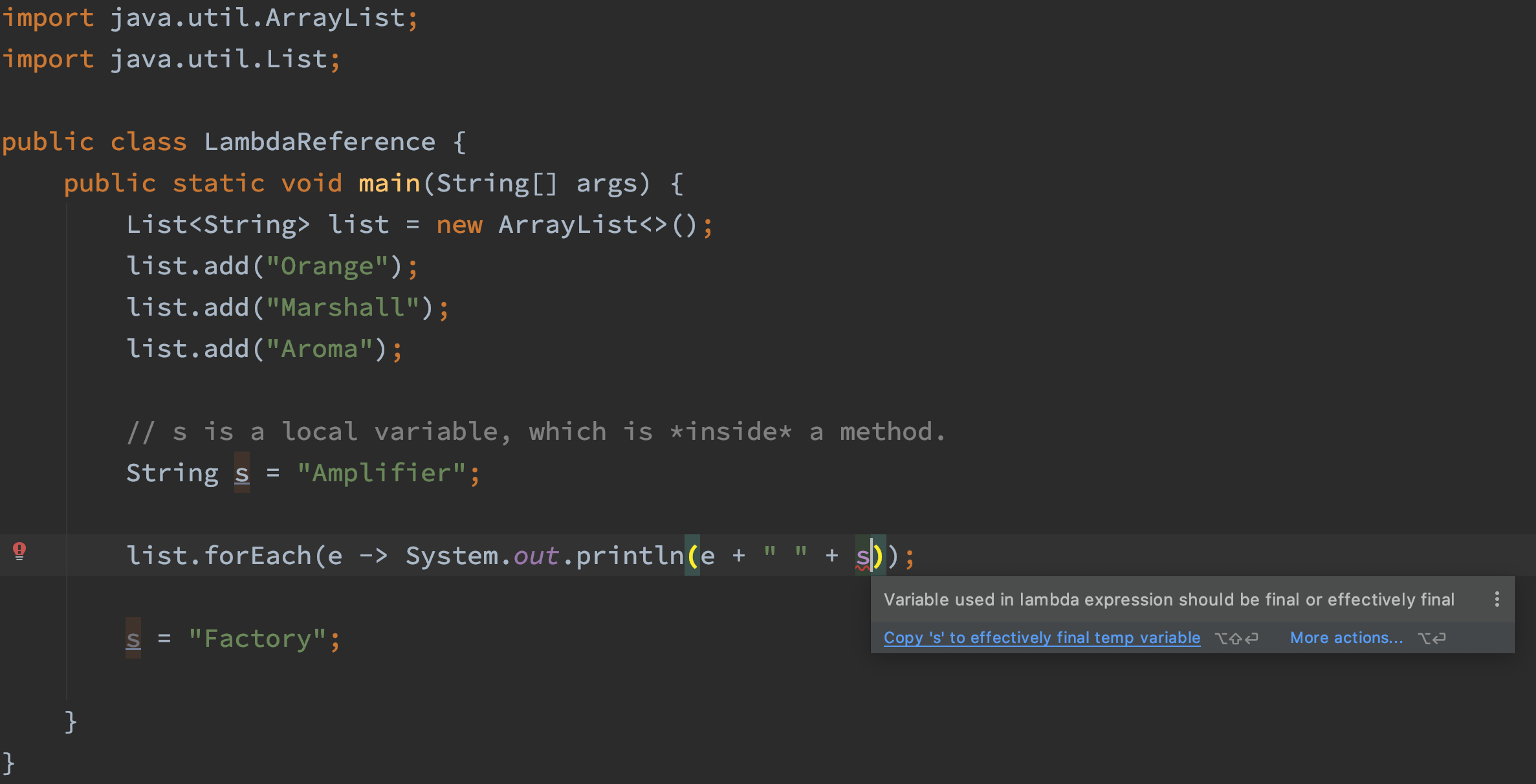
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;public class LambdaReference public static void main (String[] args) List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add("Orange" ); list.add("Marshall" ); list.add("Aroma" ); String s = "Amplifier" ; list.forEach(e -> System.out.println(e + " " + s)); } }
In the above code, the lambda function references a local variable s, and the output of the code is:
1 2 3 Orange Amplifier Marshall Amplifier Aroma Amplifier
In this case, the variable s should be effectively final , which means that we cannot change its value. If we change its value from “Amplifier” to “Factory”, there would be an error:
Therefore, a more clean and straightfoward way is to declare the variable s as a final variable:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;public class LambdaReference public static void main (String[] args) List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add("Orange" ); list.add("Marshall" ); list.add("Aroma" ); final String s = "Amplifier" ; list.forEach(e -> System.out.println(e + " " + s)); } }
Another thing worth noting is that, a variable of reference type is considered effectively final if the reference does not change, even if the object itself is mutable and changes. For example:
1 2 3 4 TreeSet<Employee> set = new TreeSet<Employee>(); list.forEach( entry -> set.add(entry) );
Reference an instance variable A lambda expression can also reference an instance variable:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;public class LambdaReference String s = "Amplifier" ; public void foo () List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add("Orange" ); list.add("Marshall" ); list.add("Aroma" ); list.forEach(e -> System.out.println(e + " " + s)); } public static void main (String[] args) LambdaReference lr = new LambdaReference(); lr.foo(); } }
In the above code, s is an instance variable, and the output of the code is:
1 2 3 Orange Amplifier Marshall Amplifier Aroma Amplifier
Note that s does not have to be final or effectively final, which means that we can change the value of s:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;public class LambdaReference String s = "Amplifier" ; public void foo () List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add("Orange" ); list.add("Marshall" ); list.add("Aroma" ); list.forEach(e -> System.out.println(e + " " + s)); System.out.println("----------------------------" ); s = "Factory" ; list.forEach(e -> System.out.println(e + " " + s)); } public static void main (String[] args) LambdaReference lr = new LambdaReference(); lr.foo(); } }
The output is:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Orange Amplifier Marshall Amplifier Aroma Amplifier ---------------------------- Orange Factory Marshall Factory Aroma Factory
Reference a static variable Similar to instance variable, static variable can be referenced by instance variable, and it needs not to be final or effectively final:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;public class LambdaReference static String s = "Amplifier" ; public static void main (String[] args) List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add("Orange" ); list.add("Marshall" ); list.add("Aroma" ); list.forEach(e -> System.out.println(e + " " + s)); System.out.println("----------------------------" ); s = "Factory" ; list.forEach(e -> System.out.println(e + " " + s)); } }
The output of the above code is:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Orange Amplifier Marshall Amplifier Aroma Amplifier ---------------------------- Orange Factory Marshall Factory Aroma Factory